Heading into the winter months, few things matter more than an efficient and reliable home heating system. For many homeowners, that means relying on forced air heating, one of the most common and effective ways to keep indoor spaces warm. But how exactly does a forced air system work, and what makes it different from other heating options?
This article will help you understand forced air heating systems, their advantages, and the best ways to maintain them for long-term comfort and efficiency.
What Is Forced Air Heating?
A forced air heating system uses heated air to warm your home. It works by heating air inside a furnace/air handler and distributing it through a network of ductwork and vents. Once the air cools, it’s pulled back into the furnace/air handler through return ducts, reheated, and circulated again, creating a consistent and comfortable indoor temperature.
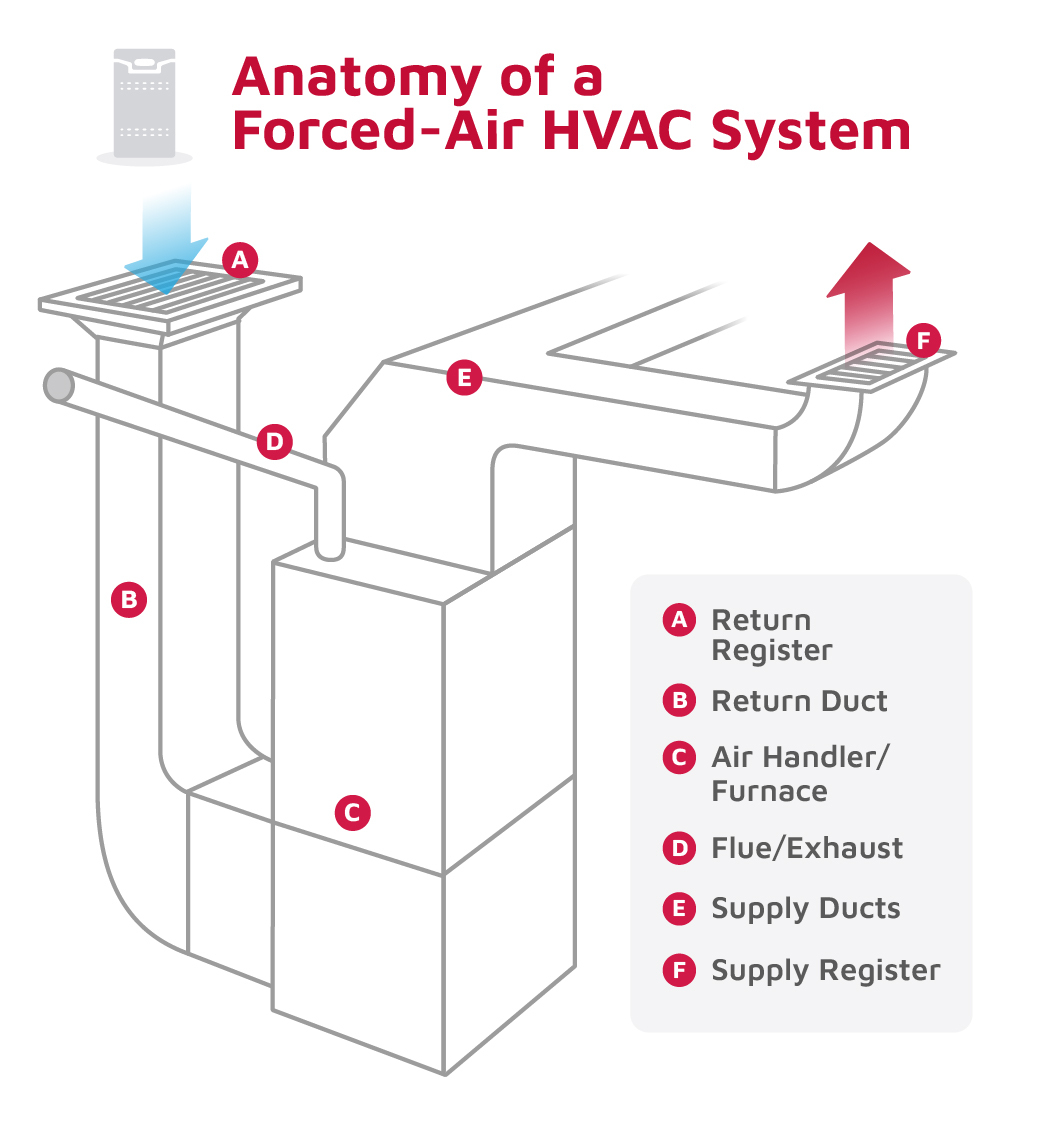
Key Components of a Forced Air System
- Furnace: The main heating source, powered by natural gas, propane, or oil.
- Air Handler: The main heating source powered by electricity
- Blower Fan: Pushes the warm air through ductwork and vents.
- Ductwork: The network of air channels that distributes heat throughout the home.
- Supply and Return Vents: Supply vents deliver heated air into rooms, while return vents pull cool air back into the system to be reheated.
- Thermostat: Controls temperature settings and tells the furnace/air handler when to turn on or off.
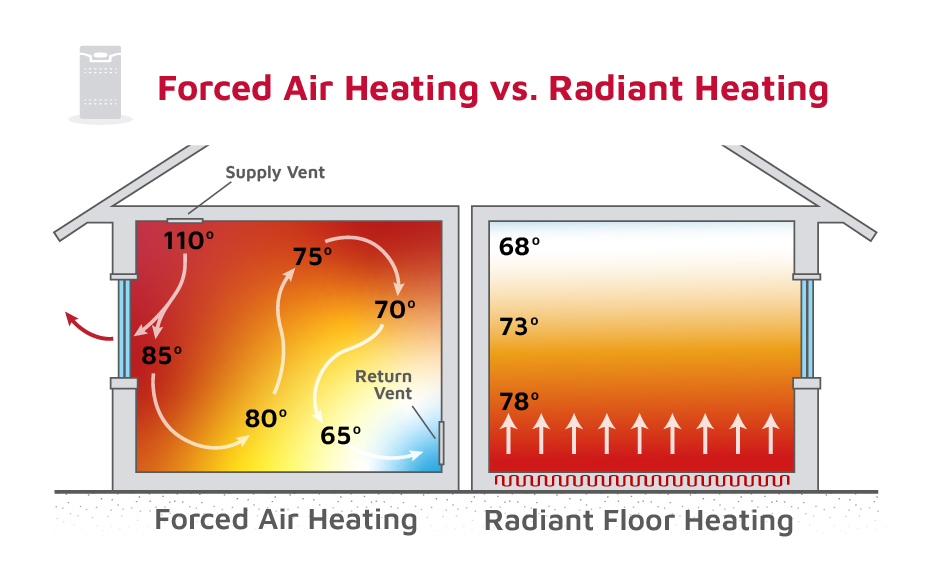
How It Differs from Other Heating Systems?
Unlike radiant heating systems that rely on hot water pipes or radiators, forced air systems heat and move air, allowing them to deliver warmth quickly. They also integrate easily with air conditioning systems, air filters and purifiers, and humidifiers, making them a versatile option for year-round comfort.
How Forced Air Heating Works?
The heating process begins when your thermostat senses that the indoor temperature has dropped below your set point. Here’s how the system responds:
- Heating: The furnace ignites or the air handler activates its heating element.
- Distribution: The blower fan pushes the warmed air through the ductwork.
- Delivery: Heated air exits through vents in each room, while cooler air is drawn back through centrally located return ducts.
- Cycle Repeat: This cycle continues until your thermostat detects the desired temperature.
Because air moves continuously through the system, you’ll notice an even distribution of warmth and a faster response compared to other heating methods.
Benefits of Forced Air Heating
Fast and Consistent Heating
Forced air systems warm up your home quickly since heated air moves through ducts and vents almost immediately after the system turns on.
Cost Savings
With regular maintenance, a forced air system can help keep energy costs manageable during the colder months.
Year-Round Climate Control
Forced air systems can be paired with central air conditioning or heat pumps, and air purification systems. This means one integrated network of ducts can handle heating, cooling, and air filtration for your entire home.
Better Air Quality and Humidity Control
With the addition of high-efficiency filters or whole-home humidifiers, forced air systems can improve indoor air quality by removing dust, allergens, and dry air during the heating season.
Potential Drawbacks to Be Aware Of
While forced air systems are efficient and reliable, there are a few considerations:
- Noise: The sound of air moving through ducts or the equipment turning on may be noticeable in older systems.
- Dust and Allergen Circulation: Because air is constantly moving, it can also circulate dust and allergens if filters aren’t cleaned or replaced regularly.
- Duct Maintenance :Leaky or poorly insulated ducts can lead to energy loss and uneven heating.
These issues are typically easy to prevent with regular inspections and filter maintenance.
Maintaining a Forced Air Heating System
Routine maintenance keeps your system running efficiently and helps extend its lifespan.
Follow these best practices:
- Replace Filters Regularly: Change air filters every one to three months, depending on usage and household requirements.
- Inspect Ductwork for Leaks: Leaks reduce efficiency and can cause uneven heating. Sealing and insulating ducts helps maintain consistent temperatures.
- Schedule Annual System Tune-Ups: A professional inspection ensures your equipment is operating correctly and safely.
- Keep Vents Clear: Make sure furniture and rugs aren’t blocking airflow from supply or return vents.
Signs It’s Time for Service
If you notice rising utility bills, weak airflow, or unusual noises, it may be time to call in a professional. They can evaluate the system, check components, and make any necessary repairs before small issues become costly problems.
The Comfort Advantage of Forced Air Heating
Forced air heating remains one of the most popular home heating solutions because it’s fast, efficient, and adaptable. When properly maintained, it provides steady warmth, improved air quality, and the ability to integrate with other comfort-enhancing systems like central cooling and smart thermostats.
If you’re considering upgrades or new system options, reach out to your local Lennox professional for a consultation. They’ll assess your space and help you find the components that best meet your needs.

