A Homeowner’s Guide to Choosing the Right System
Selecting a new furnace is one of the most important decisions a homeowner makes about their heating system. The choice between a gas furnace and an electric furnace affects comfort, utility costs, long-term maintenance, and how well the home performs during cold weather. It’s important to understand how each system works and where each option excels when choosing the best system for your home—taking climate, energy source, budget and other factors into consideration.
How Gas and Electric Furnaces Work?
Gas furnaces generate heat by burning natural gas or propane. The heat from combustion warms a heat exchanger, and a blower pushes warm air through the ductwork. These systems are known for powerful heat output and the ability to raise indoor temperatures quickly. Homes with access to affordable natural gas often find gas furnaces cost-effective to operate.
An electric furnace produces heat using electric heating elements, similar to large-scale versions of electric space heaters. This process is called electric resistive heating. Air passes over heated coils and is distributed through the home. Electric furnaces do not require a gas line or venting, which can simplify installation. They are a practical option for homes that rely exclusively on electricity or lack access to natural gas.
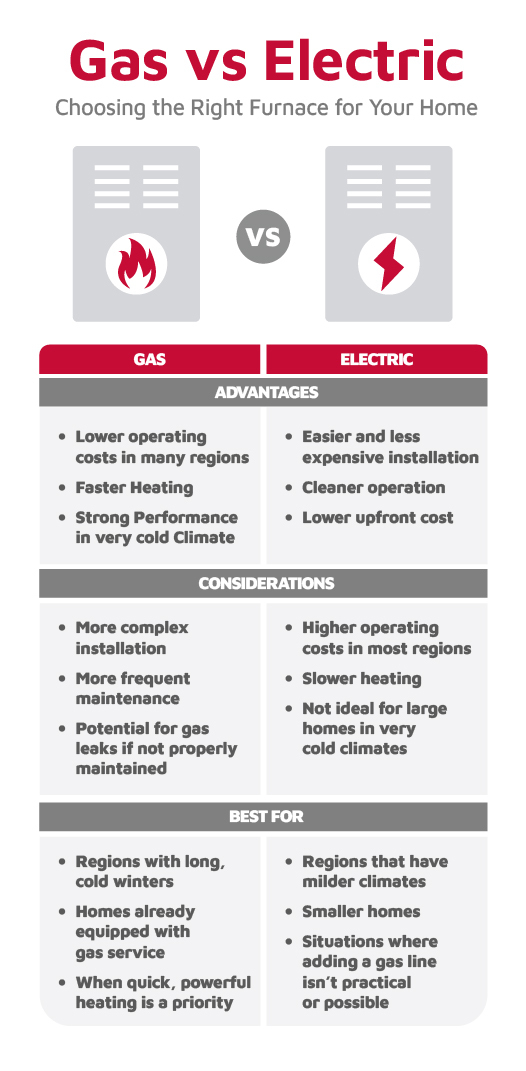
Advantages and Considerations of a Gas Furnace
Advantages
- Lower operating costs in many regions: Natural gas is often cheaper than electricity, resulting in lower heating bills.
- Faster heating: Gas furnaces produce higher temperatures, which helps warm large spaces quickly.
- Strong performance in very cold climates: These systems maintain heat output even during extreme winter temperatures.
Considerations
- More complex installation: A gas line, proper venting, and adherence to safety codes are required.
- More frequent maintenance: Gas furnaces need routine inspections to check for combustion issues, carbon monoxide risks, and heat exchanger condition.
- Potential for gas leaks if not properly maintained: Professional servicing is essential for safety.
Gas furnaces work well in regions with long, cold winters and in homes already equipped with gas service. They are also ideal when quick, powerful heating is a priority.
Advantages and Considerations of Electric Furnaces
Advantages
- Easier and less expensive installation: No gas line, no venting, and fewer components.
- Cleaner operation: No combustion gases or carbon monoxide, which simplifies safety considerations.
- Lower upfront cost: Electric furnaces are generally less expensive to purchase and install.
Considerations
- Higher operating costs in most regions: Heating with electric resistive heat often costs more than using natural gas.
- Slower heating response: Electric elements warm the air gradually.
- Not ideal for large homes in very cold climates: Electric resistive heating can struggle to keep up with extreme temperatures without higher energy use.
Electric systems are suited to smaller homes, milder climates, or situations where adding a gas line is not possible or practical.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Furnace
Every home is unique. When choosing the right furnace for your home, there are some important things to consider.
- Home Size and Layout: Large homes often benefit from the stronger heat output of a gas furnace. Smaller or well-insulated homes may perform well with an electric option.
- Climate: Cold climates typically favor gas furnaces because they maintain heating capacity during very low outdoor temperatures. Electric furnaces can be efficient in mild climates with shorter heating seasons.
- Energy Costs: Local utility rates play a major role in long-term operating costs. If the cost of electricity is significantly higher than natural gas in your area, a gas system may offer more budget-friendly heating.
- Existing Infrastructure: If your home already has a gas line, sticking with a gas furnace often makes installation simpler. Homes without gas service may lean toward electric unless they plan to add gas access.
- Considering a Switch from Gas to Electric: Switching from gas to electric can offer cleaner operation or simplify maintenance but may increase energy costs. Homeowners considering a fuel-type change should weigh utility rates, climate, and installation requirements.
Make the Right Choice for Your Home
Choosing between a gas and electric furnace is not about which system is universally “better,” but which one best aligns with your home, climate, and long-term heating needs. Understanding how each furnace type performs, what it costs to operate, and what installation requires can help you reach a more informed decision.
If you are unsure which system is right for your home, connecting with a qualified HVAC professional is the most reliable way to evaluate your heating needs. A trained technician can assess your home’s layout, insulation, climate, and energy usage to recommend the most suitable and efficient option.
A properly selected furnace can provide consistent comfort, support lower energy use, and keep your home warm through many winters ahead.

